
Integrating observations and measurements from Parker Solar Probe, Solar Orbiter, and other space- and ground-based observatories — The launch of Parker Solar Probe (PSP) in 2018, followed by Solar Orbiter (SO) in February 2020, has opened a new window in the exploration of solar magnetic activity and the origin of the heliosphere.
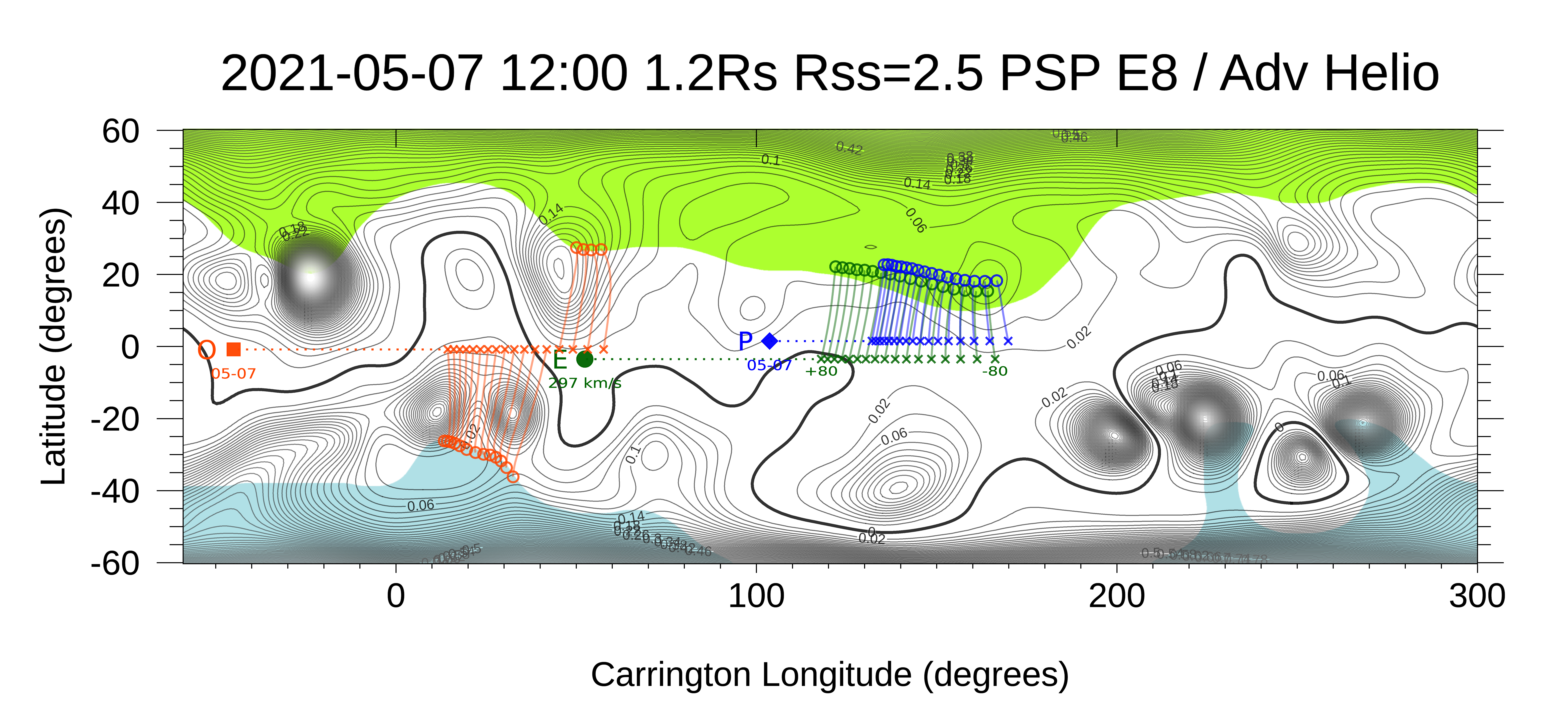
Exploring Solar Wind Origins and Connecting Plasma Flows from the Parker Solar Probe to 1 au — The magnetic field measurements of the FIELDS instrument on the Parker Solar Probe (PSP) have shown intensities, throughout its first solar encounter, that require a very low source surface (SS) height to be reconciled with
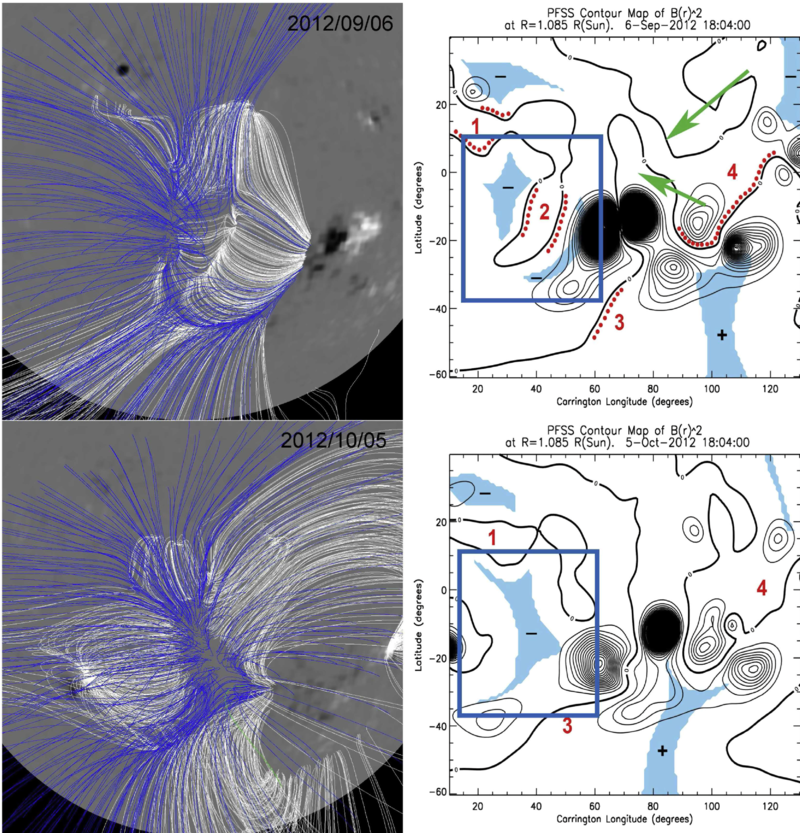
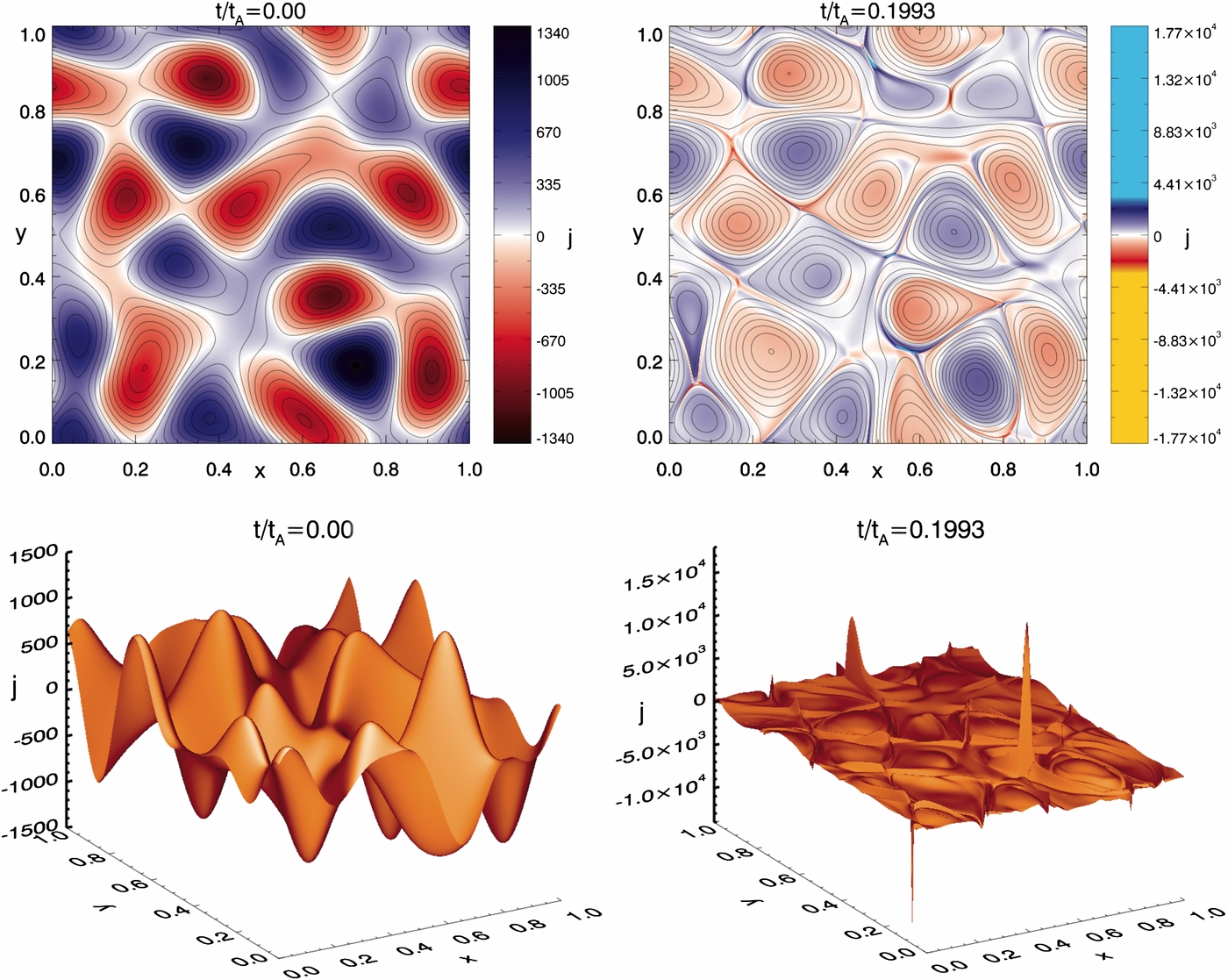
Large-scale Magnetic Funnels in the Solar Corona — We describe open coronal magnetic fields with a specific geometry - large-scale coronal magnetic funnels - that are found to play an important role in coronal dynamics. Coronal magnetic funnels can be attributed to three
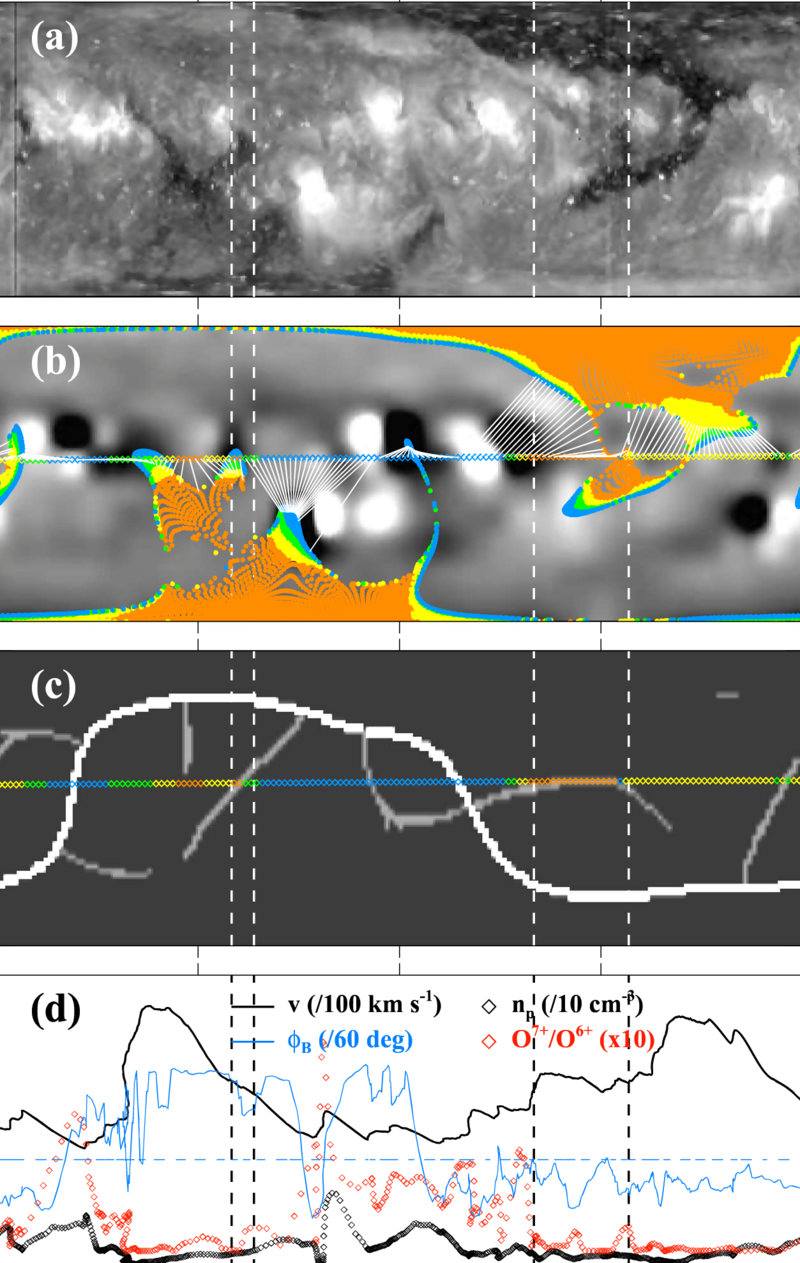
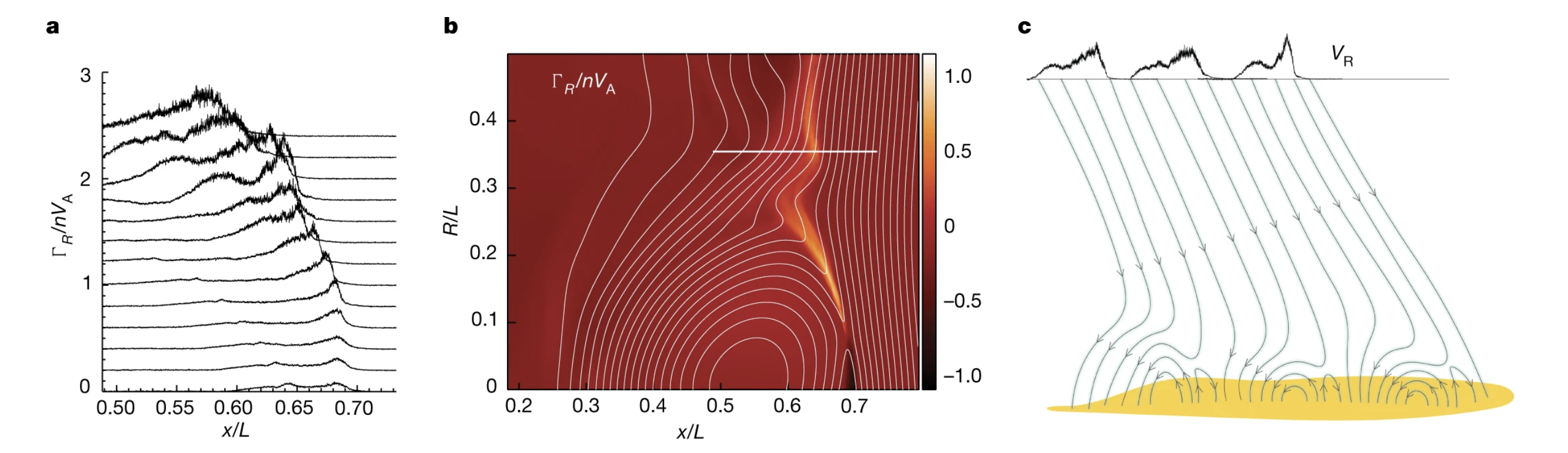
Observations of Solar Wind from Earth-directed Coronal Pseudostreamers — Low-speed (<450 km s-1) solar wind is widely considered to originate from streamer loops that intermittently release their contents into the heliosphere, in contrast to high-speed wind, which has its source in large coronal holes.
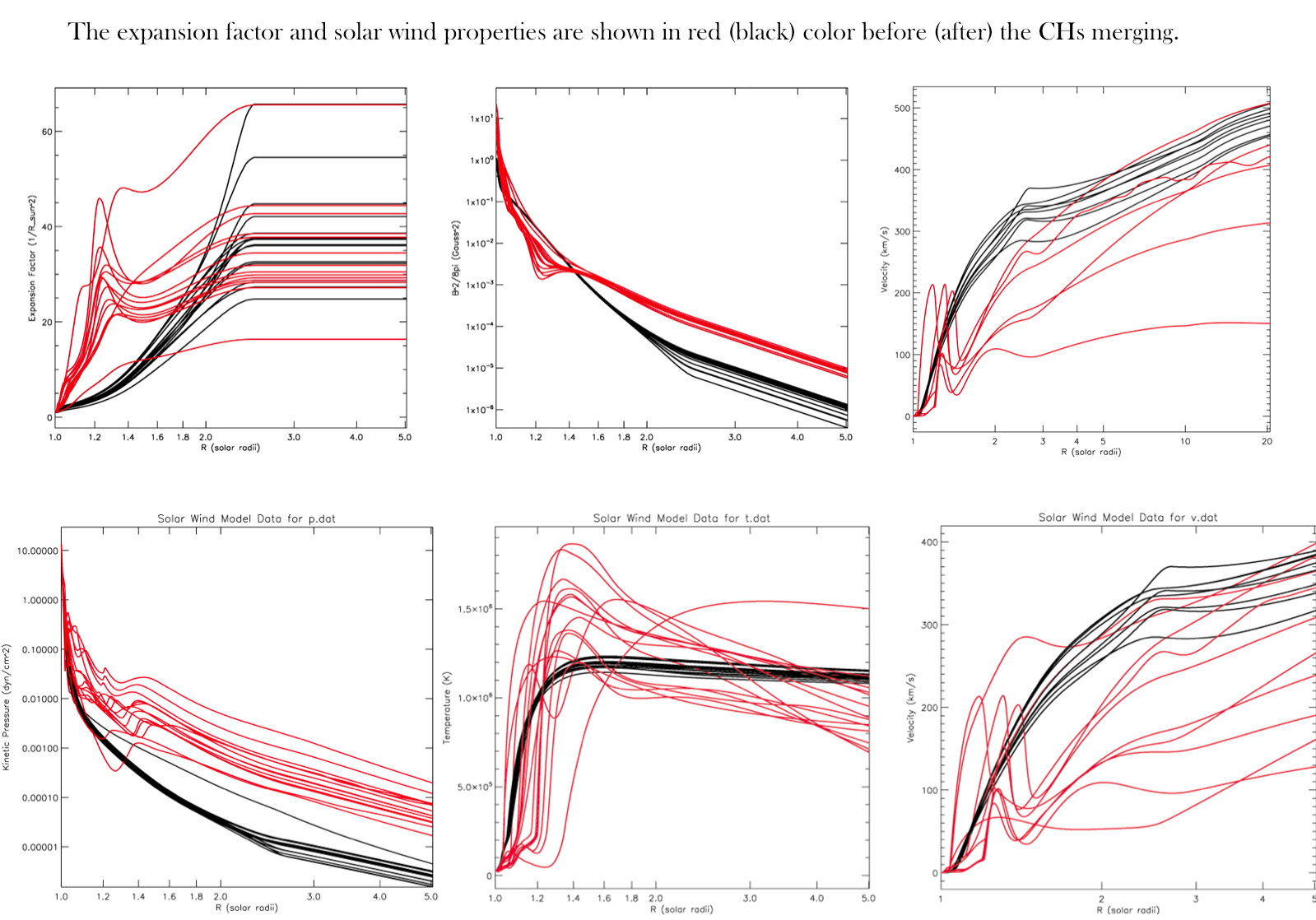
Morphology of Pseudostreamers and Solar Wind Properties — The solar dynamo and photospheric convection lead to three main types of structures extending from the solar surface into the corona - active regions, solar filaments (prominences when observed at the limb) and coronal holes.
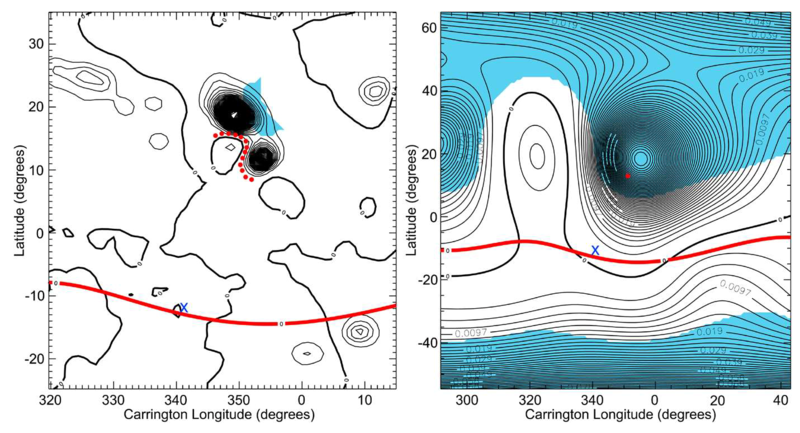
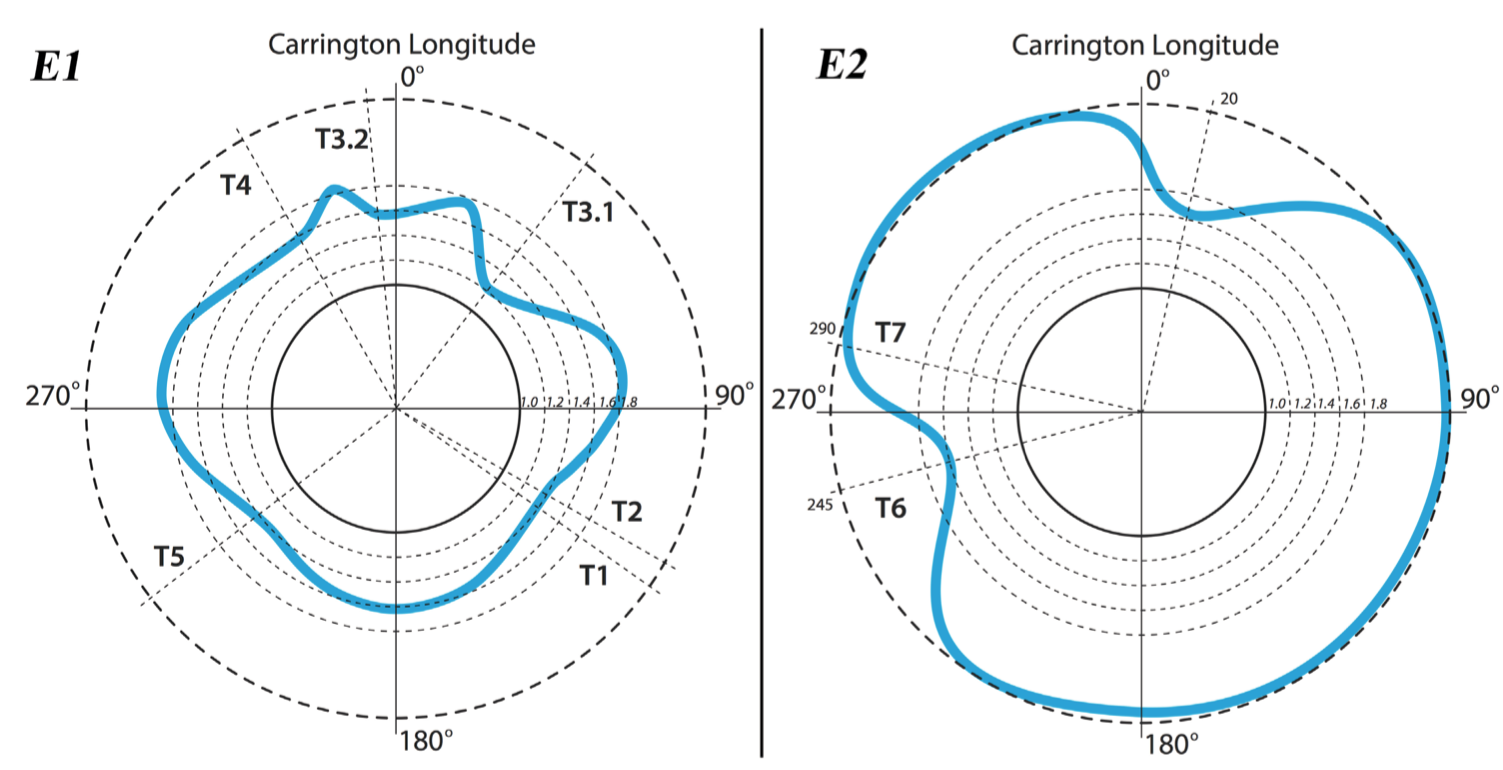
Observations and Analysis of the Non-Radial Propagation of Coronal Mass Ejections Near the Sun — The trajectories of coronal mass ejection (CME) are often observed to deviate from radial propagation from the source while within the coronagraph field of view (R <15 - 30 R_{sun}). To better understand nonradial propagation